On this article, i will explain about problem in revision of Electron Transport System in mitochondria.
The big question is : "how many ATP produced in aerobic respiration?
if you read, some source say 36/38 but the other 30/32. which one is
true?"
One day, I got a case from my tutorial class, this case talks about
Obesity and Hypercholesterol in a patient. This is the study method in
my faculty (medical faculty), we got one case every week. In med faculty
nowadays, we study from the case first and slowly begin to reach the
basic science, which is related to the case. We were forced to
understand the basic science, so we can solve the problem. This is
important because, phylosophically, in doctor's daily life they always
presented with cases from the patient.
So, lets begin..
Respiration is one of the process in organism to gain energy. So special
because this kind of process gain the biggest energy rather than the
other.
Divided into four step :
Glycolisis, Oxidative Decarboxialtion, Kreb cycle/TCA cycle, and
Electron Transport System (ETS)
(also, some said only three step, they grouped DO into TCA cycle, whatever it is, the reaction still the same)
and the ATP result :
from Campbell Biology
but, look at this too :
from Lehninger Biochemistry
The question is :
*Which one is true? 36/38 atp or 30/32 atp?
This difference make me confused, until i try to figure out what is
going on and then realize that "book released in 2006 and later" did
some kind of revision saying "
ATP produced in one complex oxidation process result 30/32 atp" (not 36/38 atp).
*But, how could this revision was made?
The key to understand this is to know in detail about Electron Transport
System process, how complex 1,2,3 and 4 work together. This main
distinction actually come from the change in understanding of how NADH /
FADH release H+ and produce ATP.
new revised chemiosmotic theory :

old theory :

so, now we use the new theory that said:
NADH gain 10 H+
FADH gain 6 H+
*But, why one Hidrogen ion result in 2.5 atp, why not integer value like 1 ATP?
Old theory said 1 H will pass ATP synthase result in 1 ATP, but now research said the system not like that.
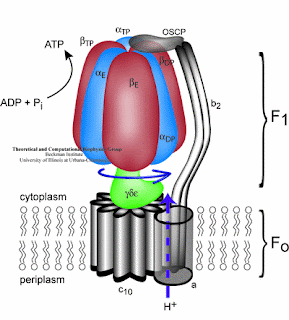
Take a look inside the new theory of ATP Synthase:
New properties of ATP synthase :
- ATP synthase is comprised of F1 and F0 molecule. F1 is alpha and
beta component, F0 is C component. where H+ will be inserted in C
component, so the C component can rotate.
- There are 12 slots for hidrogen ion in C component to be inserted. Hidrogen has to fulfill the slot so it can rotate.
- When C component rotates 360 degrees, the ATP synthase resulting 2.5 ATP.
Then, the conclusion is:
1 rotation = 3 ATP
1 rotation = need 12 hydrogen ion
12 H = 3 ATP -> 4 H = 1 ATP
NADH = resulting 10 H
(10 H / 4 H) * 1 ATP = 2.5 ATP
FADH = resulting 6 H
(6 H / 4 H) * 1 ATP = 1.5 ATP
reference :
Whitney Ellie, 2008, Understanding Nutrition 11th edition
Murray Robert K., 2009, Harper's Illustrated Biochemistry 28th edition